We know the fastest way to combine lists. Today we will try to find the fastest way to combine dictionaries
We will be considering the following ways
- Using a for loop
- Using the update() method
- Using the ChainMap Function
- Using the unpacking operator
- Using the pipe operator ( | )
- Using the (|=) operator
How are we going to measure the performance?
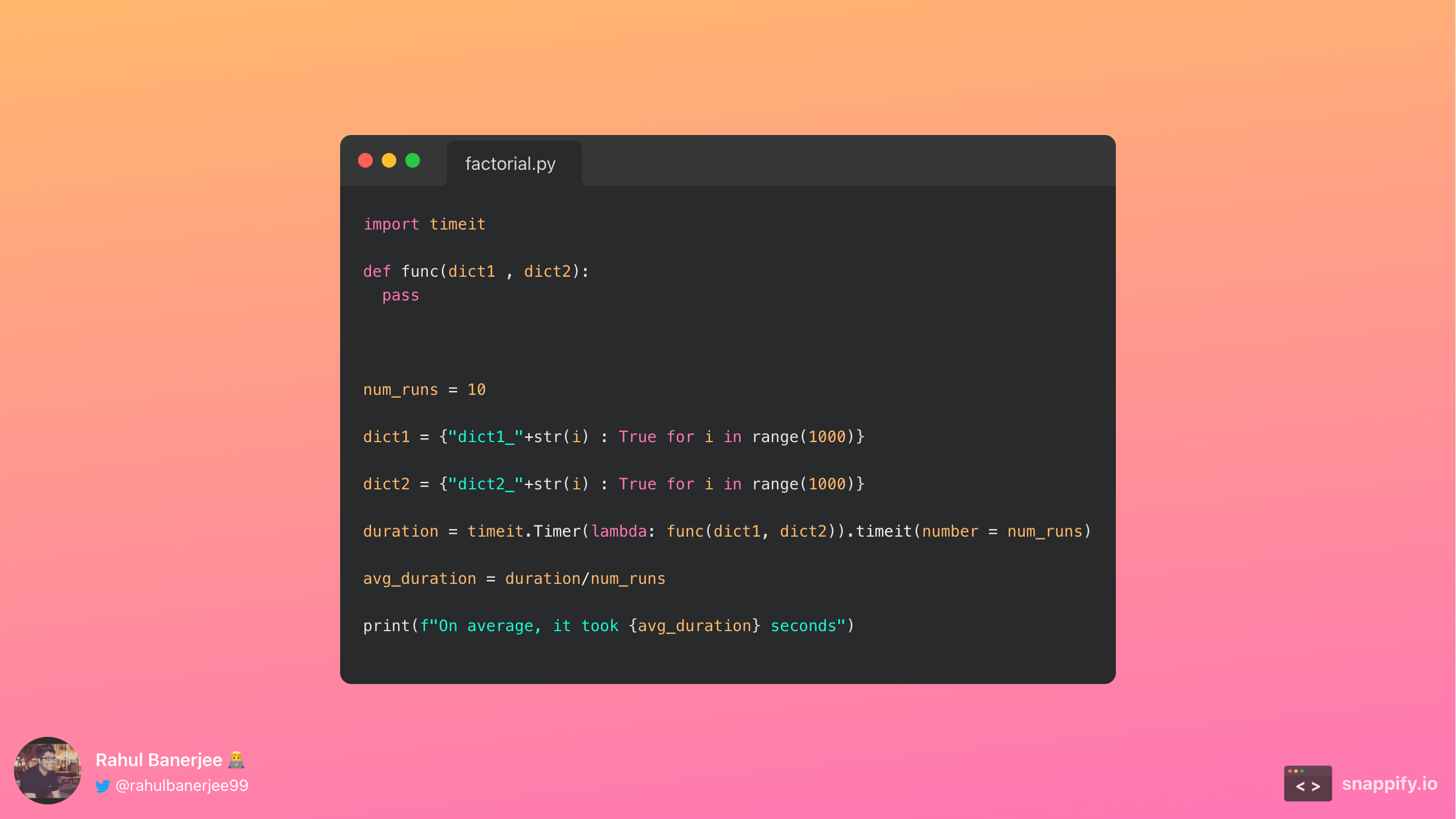
We have a couple of dictionaries with 1000 key-value pairs in each dictionary. We will update function func to perform the different combination methods. The function will be called 100 times and we will print the average run time.
Using a for loop
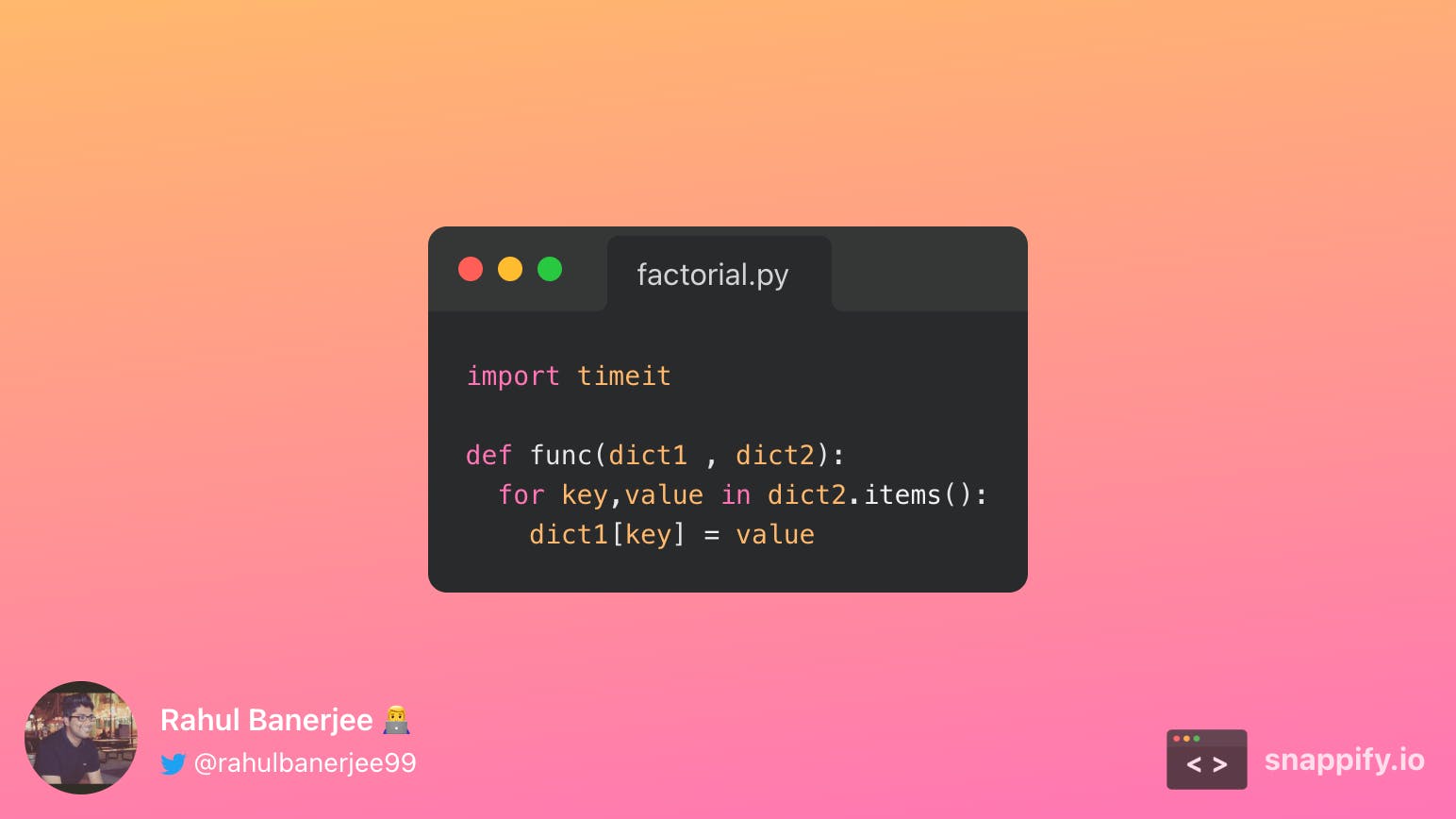
We simply iterate over the second dictionary and add its elements to the first dictionary. Below is the output
On average, it took 6.765522999558016e-05 seconds
Using the update method
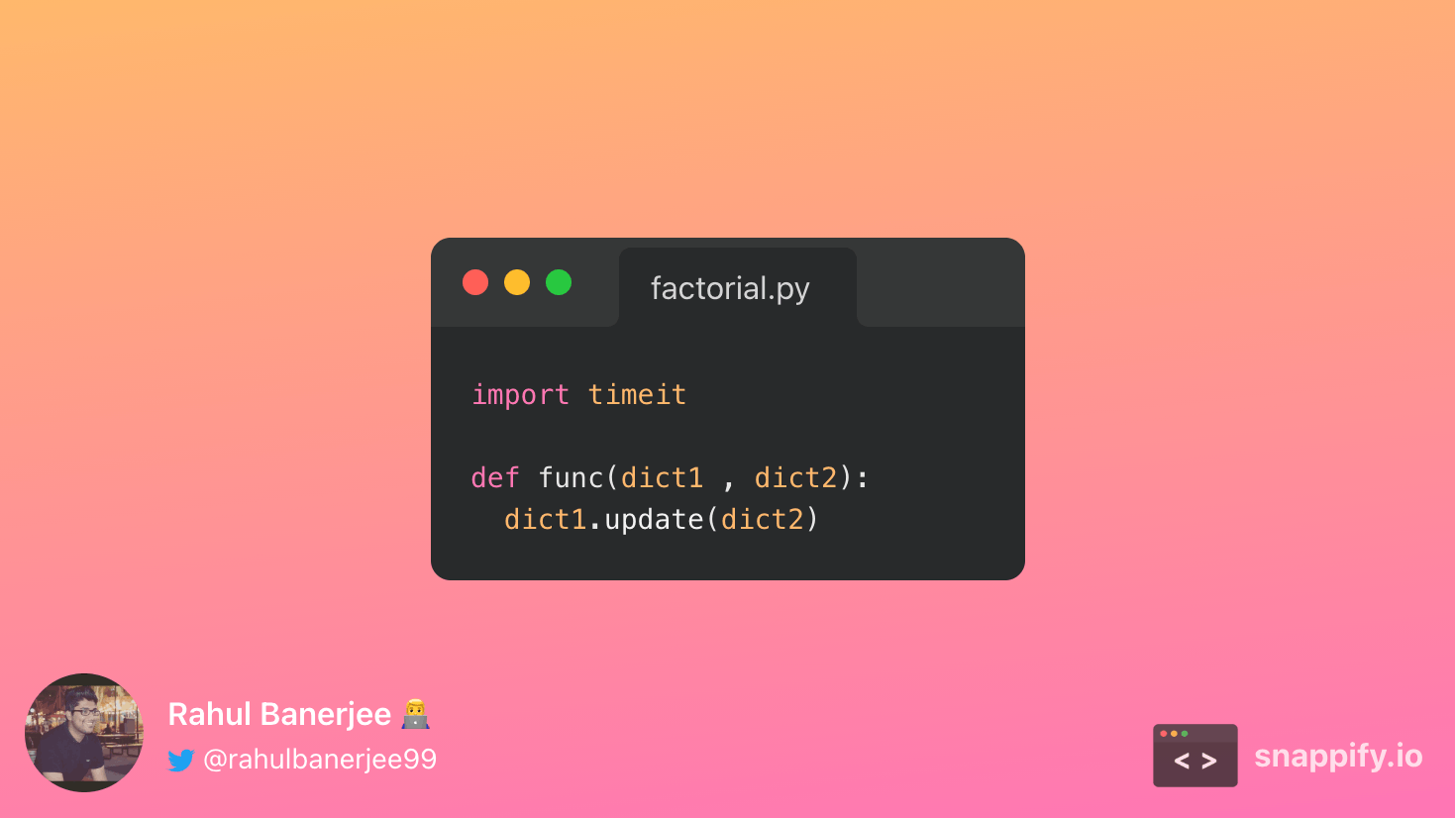
Similar to the for loop approach, the first dictionary is updated. The elements of the second dictionary are added to the first dictionary. If there is a common key present, the value for the key in the first dictionary will be overwritten by that of the second dictionary.
On average, it took 2.554959000008239e-05 seconds
Using the ChainMap Function
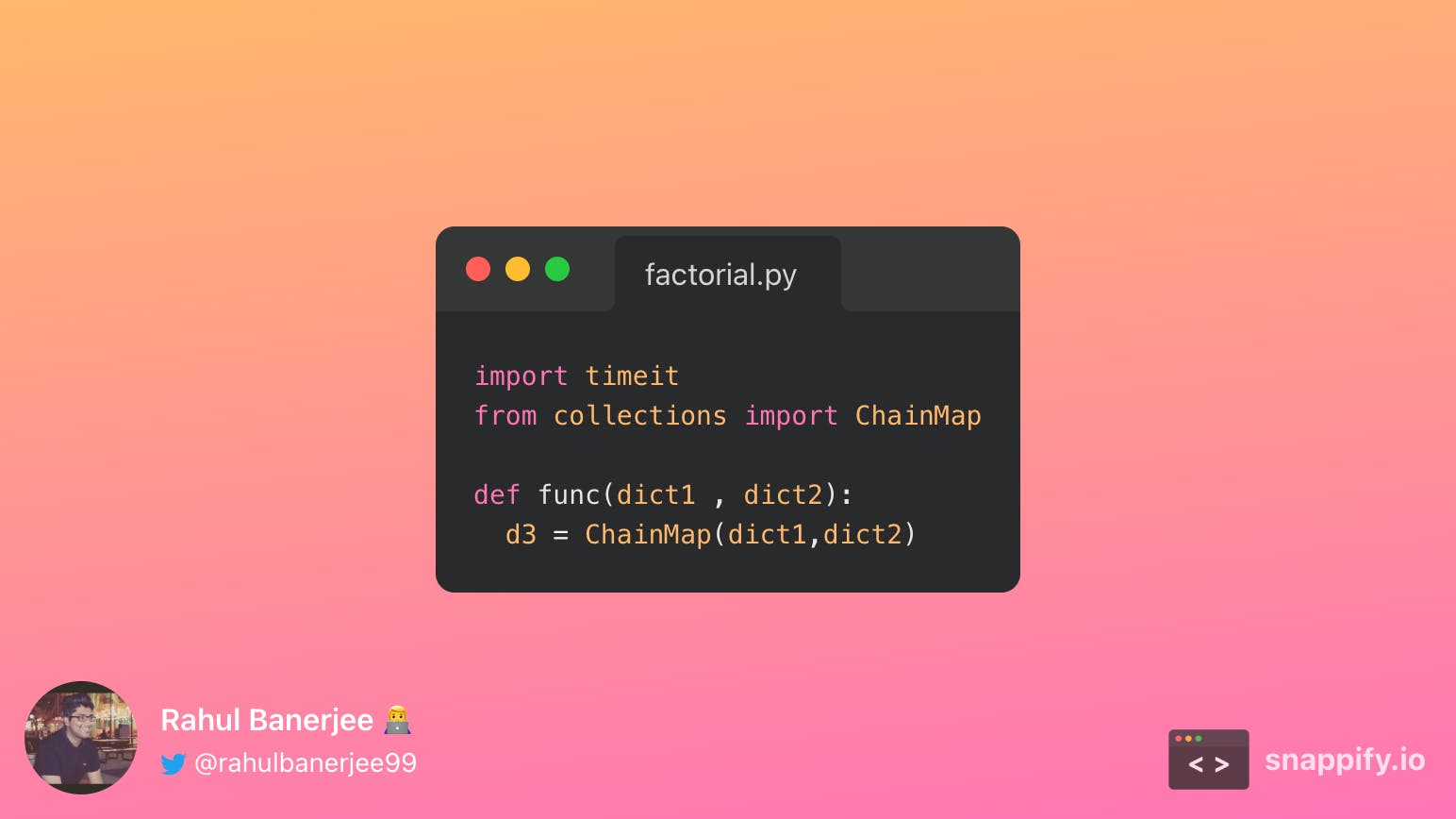 Unlike the previous two approaches, a new dictionary is created and the original dictionaries are not updated. Below is the output
Unlike the previous two approaches, a new dictionary is created and the original dictionaries are not updated. Below is the output
On average, it took 9.942399992723949e-07 seconds
Using the unpacking operator
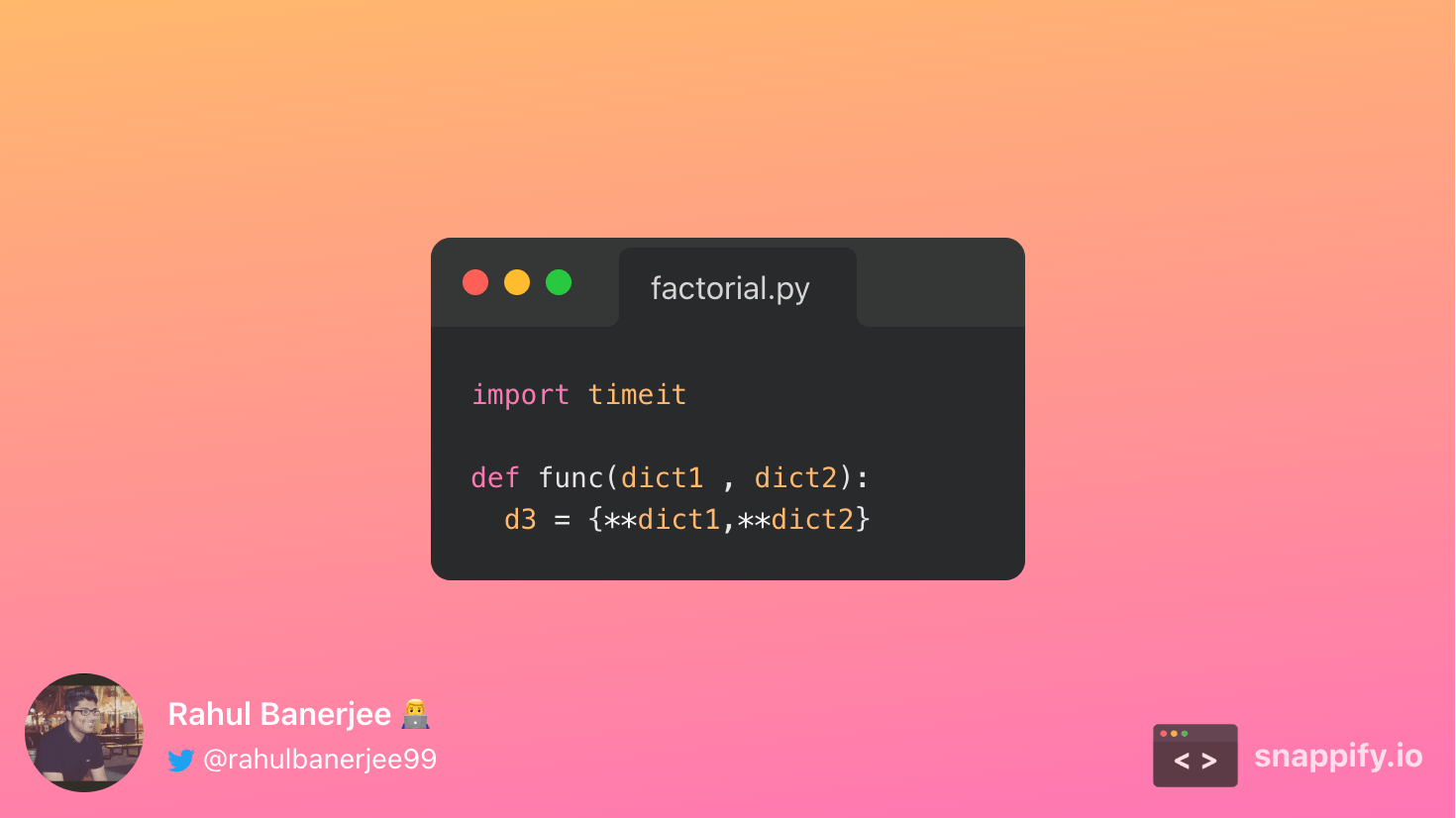
In this approach as well, we create a new dictionary. The original dictionaries are not updated. Below is the output
On average, it took 7.01560299967241e-05 seconds
Using the | operator
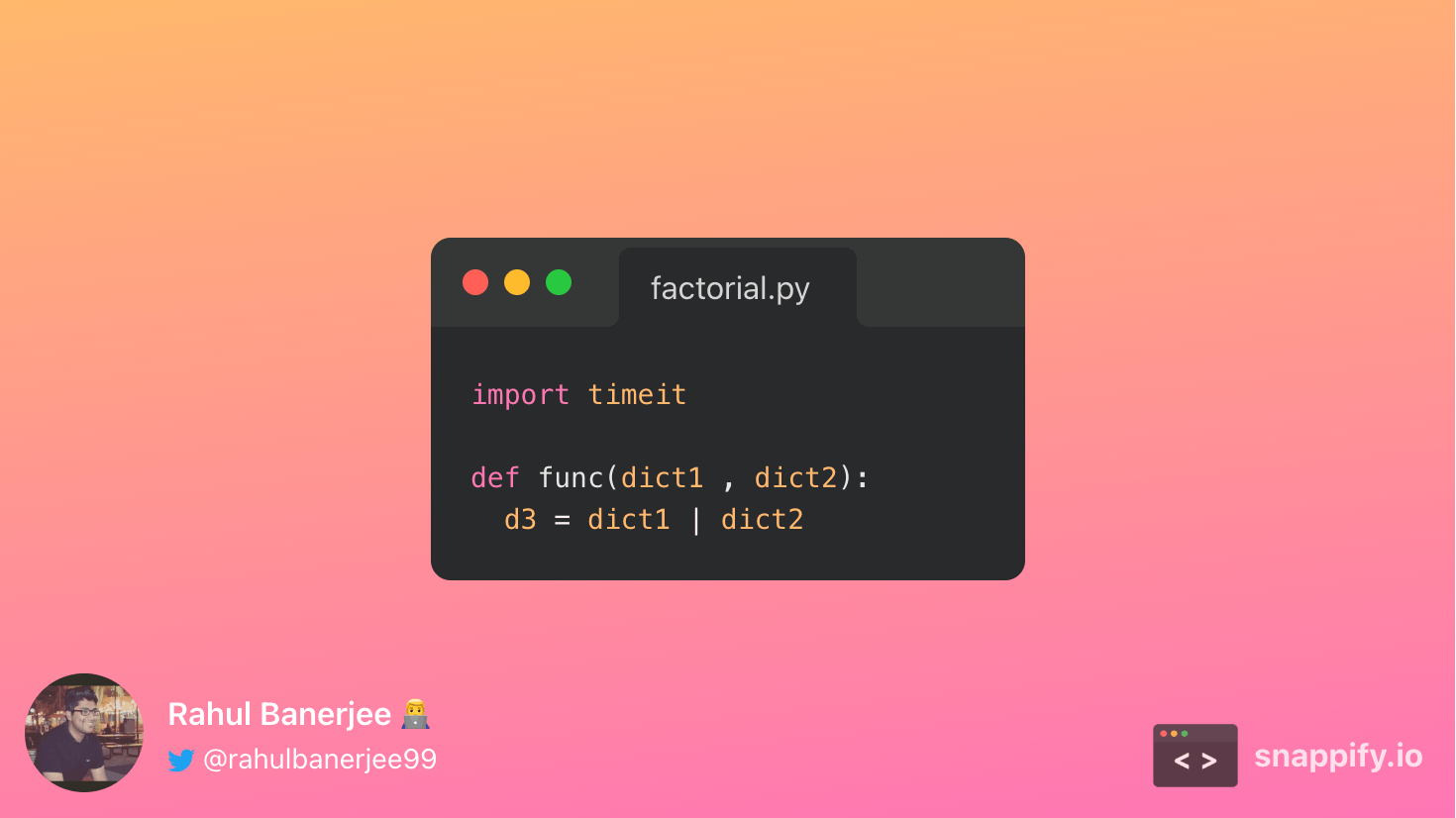
In Python 3.9, the pipe operator was introduced to combine dictionaries. Below is the output
On average, it took 5.5255000000000026e-05 seconds
Using the |= operator
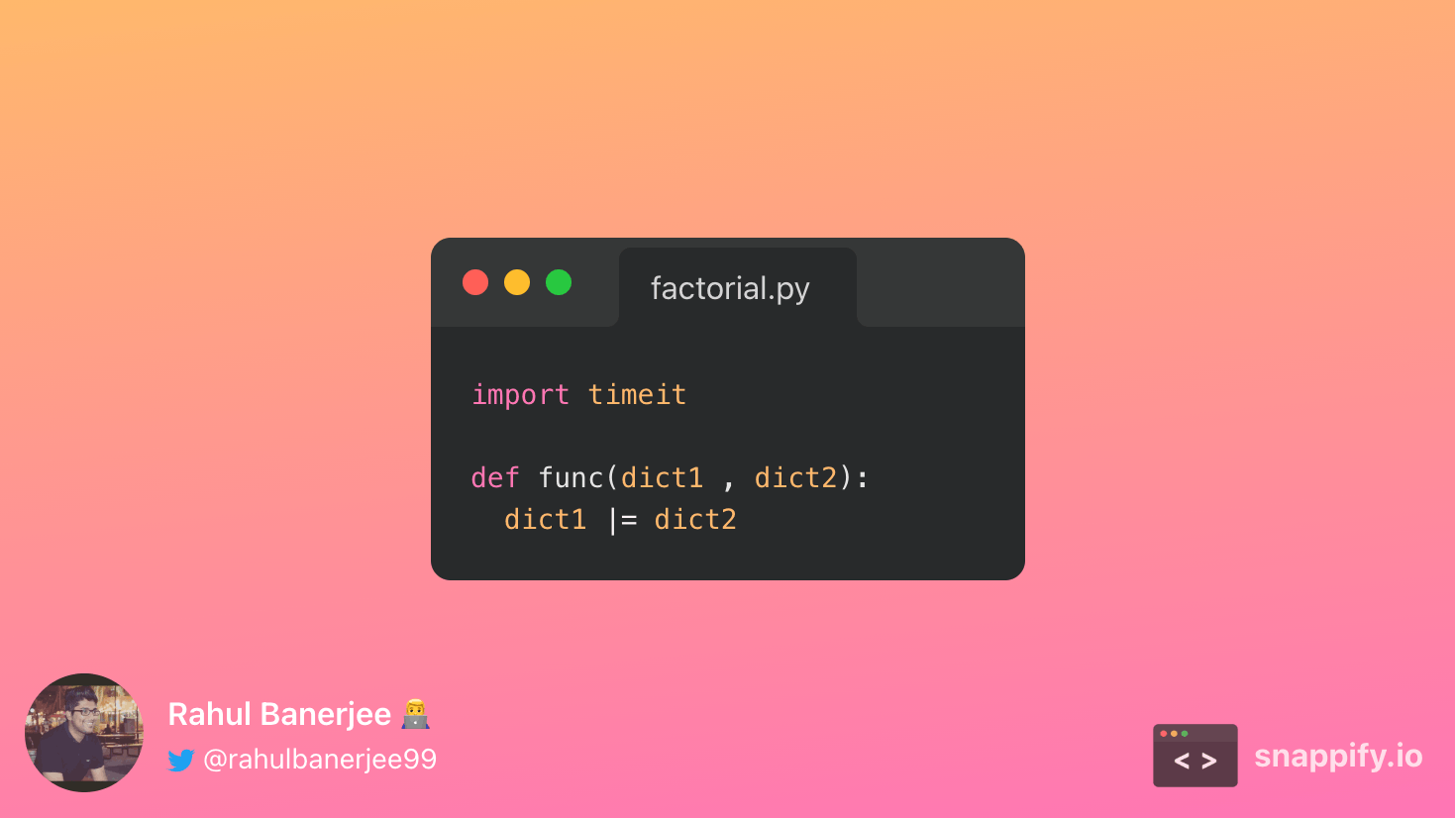
Along with the | operator, the |= operator was introduced in Python 3.9. Below is the output
On average, it took 3.0259589999999983e-05 seconds
Comparison
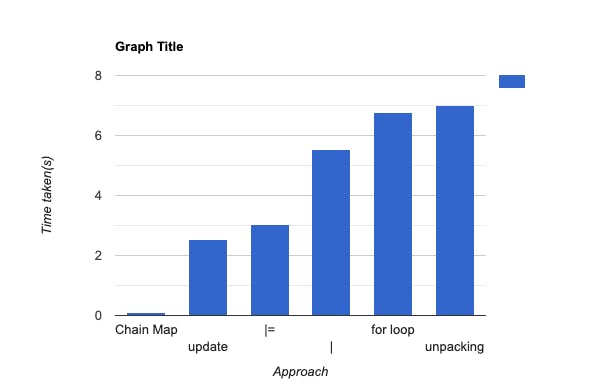
The ChainMap() method seems to be the fastest